[모던 자바스크립트 Deep Dive]40장 이벤트
40.1 이벤트 드리븐 프로그래밍
- 이벤트 핸들러: 이벤트가 발생했을 때 호출될함수
- 이벤트 핸들러 등록: 이벤트가 발생했을 때 브라우저에 이벤트 핸들러 호출을 위임하는 것
- 사용자가 언제 이벤트를 발생시킬지 모르기 때문에 이를 감지할 수 있는 브라우저에 위임
- 이벤트 드리븐 프로그래밍: 이벤트를 중심으로 프로그램의 흐름을 제어하는 프로그래밍 방식
40.2 이벤트 타입
- 이벤트 종류를 나타내는 문자열
- 약 200여 가지가 존재
40.2.1 마우스 이벤트
| 이벤트 타입 | 이벤트 발생 시점 |
|---|---|
| click | 마우스 버튼을 클릭했을 때 |
| dblclick | 마우스 버튼을 더블 클릭했을 때 |
| mousedown | 마우스 버튼을 눌렀을 때 |
| mouseup | 누르고 있던 마우스 버튼을 놓았을 때 |
| mousemove | 마우스 커서를 움직였을 때 |
| mouseenter | 마우스 커서를 HTML 요소 안으로 이동했을 때(버블링되지 않는다) |
| mouseover | 마우스 커서를 HTML 요소 안으로 이동했을 때(버블링된다) |
| mouseleave | 마우스 커서를 HTML 요소 밖으로 이동했을 때(버블링되지 않는다) |
| mouseout | 마우스 커서를 HTML 요소 밖으로 이동했을 때(버블링된다) |
40.2.2 키보드 이벤트
| 이벤트 타입 | 이벤트 발생 시점 |
|---|---|
| keydown | control, option, shift, tab, delete, enter, 방향, 문자, 숫자, 특수 문자 키를 눌렀을 때 발생 문자, 숫자, 특수 문자, enter 키는 연속적으로 발생, 그 외의 키는 한 번만 발생 |
| keypress | 문자, 숫자, 특수 문자 enter 키를 눌렀을 때만 발생 control, option, shift, tab, delete, 방향키 등에는 발생하지 않음 폐지(deprecated)되었으므로 사용을 권장하지 않음 |
| keyup | control, option, shift, tab, delete, enter, 방향, 문자, 숫자, 특수 문자 키를 놓았을 때 발생 |
40.2.3 포커스 이벤트
| 이벤트 타입 | 이벤트 발생 시점 |
|---|---|
| focus | HTML 요소가 포커스를 받았을 때(버블링되지 않는다) |
| blur | HTML 요소가 포커스를 잃었을 때(버블링되지 않는다) |
| focusin | HTML 요소가 포커스를 받았을 때(버블링된다) 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식으로 등록하면 크롬, 사파리에서 정상동작하지 않는다. |
| addEventListener 메서드 방식을 사용해 등록해야 한다. | |
| focusout | HTML 요소가 포커스를 잃었을 때(버블링된다) 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식으로 등록하면 크롬, 사파리에서 정상동작하지 않는다. |
| addEventListener 메서드 방식을 사용해 등록해야 한다. |
40.2.4 폼 이벤트
| 이벤트 타입 | 이벤트 발생 시점 |
|---|---|
| submit | form 요소 내의 input(text, checkbox, radio), select 입력 필드(textarea 제외)에서 엔터 키를 눌렀을 때 form 요소 내의 submit 버튼( <button>, <input type=”submit”>)을 클릭했을 때위 두 경우에 form 요소에서 발생한다. |
| reset | form 요소 내의 reset 버튼을 클릭했을 때 최근에는 사용하지 않는다. |
40.2.5 값 변경 이벤트
| 이벤트 타입 | 이벤트 발생 시점 |
|---|---|
| input | input(text, checkbox, radio), select, textarea 요소의 값이 입력되었을 때 사용자가 입력하고 있을 때 발생 |
| change | input(text, checkbox, radio), select, textarea 요소의 값이 변경되었을 때 HTML 요소가 포커스를 잃었을 때 사용자 입력이 종료되었다고 인식하여 발생 사용자 입력이 종료되어 값이 변경되면 발생 |
| readystatechange | document.readyState 프로퍼티 값(loading, interactive, complete)이 변경될 때 document.readyState 프로퍼티 값은 HTML 문서의 로드와 파싱을 나타낸다. |
40.2.6 DOM 뮤테이션 이벤트
| 이벤트 타입 | 이벤트 발생 시점 |
|---|---|
| DOMContentLoaded | HTML 문서의 로드와 파싱이 완료되어 DOM 생성이 완료되었을 때 |
40.2.7 뷰 이벤트
| 이벤트 타입 | 이벤트 발생 시점 |
|---|---|
| resize | 브라우저 윈도우(window)의 크기를 리사이즈할 때 연속적으로 발생 오직 window 객체에서만 발생 |
| scroll | 웹페이지(document) 또는 HTML 요소를 스크롤할 때 연속적으로 발생 |
40.2.8 리소스 이벤트
| 이벤트 타입 | 이벤트 발생 시점 |
|---|---|
| load | DOMContentLoaded 이벤트 발생 후 모든 리소스(이미지, 폰트 등)의 로딩이 완료되었을 때 주로 window 객체에서 발생 |
| unload | 리소스가 언로드될 때 주로 새로운 웹페이지를 요청한 경우 |
| abort | 리소스 로딩이 중단되었을 때 |
| error | 리소스 로딩이 실패했을 때 |
40.3 이벤트 핸들러 등록
이벤트 핸들러를 등록하는 데에는 세 가지 방법이 있다.
- 이벤트 핸들러: 이벤트 발생 시 브라우저에 호출을 위임한 함수
40.3.1 이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트 방식
이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트 값으로 함수 호출문 등의 문을 할당하면 이벤트 핸들러가 등록된다.
- 이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트: HTML 요소의 어트리뷰트에 존재
- 이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트 이름:
on접두사 + 이벤트 종류를 나타내는 이벤트 타입
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
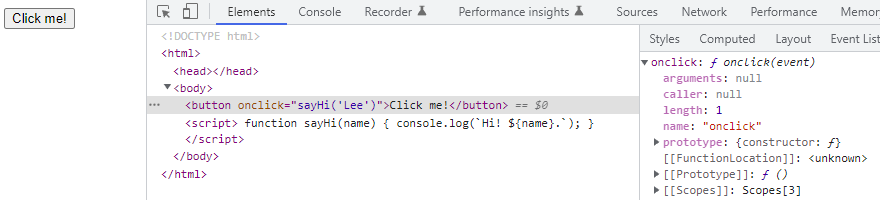
<button onclick="sayHi('Lee')">Click me!</button>
<script>
function sayHi(name) {
console.log(`Hi! ${name}.`);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트 값의 동작
- 콜백 함수처럼 함수 참조를 등록해야 브라우저가 이벤트 핸들러를 호출할 수 있다.
- 함수 참조가 아닌 호출문을 등록하면 호출문의 평가 결과가 이벤트 핸들러로 등록된다.
- 따라서 함수를 반환하는 함수가 아닌 이상 함수 호출문을 이벤트 핸들러로 등록하면 브라우저가 이를 호출할 수 없다.
- 하지만 위 예제에서 이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트 값으로 함수 호출문을 할당한다.
- 즉 이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트 값은 암묵적으로 생성될 이벤트 핸들러의 함수 몸체를 의미한다.
- 어트리뷰트는 파싱되어 암묵적으로 함수를 생성하고 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티에 할당한다.
1
2
3
4
5
// onclick="sayHi('Lee')" 어트리뷰트는 파싱되어 아래 함수를 암묵적으로 생성한다.
function onclick(event) {
sayHi('Lee');
}
// 그다음 키가 onclick인 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티에 할당한다.
- 이벤트 핸들러에 인수를 전달하기 위해 이러한 방식으로 동작
함수 참조를 할당한다면 인수를 전달하기 어렵다.
1 2
<!-- 이벤트 핸들러에 인수를 전달하기 곤란하다. --> <button onclick="sayHi">Click me!</button>
여러 개의 문을 할당할 수 있다.
1
<button onclick="console.log('Hi! '); console.log('Lee');">Click me!</button>
이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트 방식은 권장하지 않는다.
- HTML과 자바스크립트는 관심사가 다르므로 분리하는 게 좋다.
- 하지만 CBD(Component Based Development) 방식의 프레임워크/라이브러리(Angular, React, Svelte, Vue.js)에선 이 방식으로 이벤트를 처리한다.
- CBD에서는 HTML, CSS, 자바스크립트가 각각 관심사가 다른 개별적인 요소가 아닌, 뷰를 구성하기 위한 구성 요소로 보기 때문에 관심사가 다르다고 생각하지 않는다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
<!-- Angular --> <button (click)="handleClick($event)">Save</button> { /* React */ } <button onClick={handleClick}>Save</button> <!-- Svelte --> <button on:click={handleClick}>Save</button> <!-- Vue.js --> <button v-on:click="handleClick($event)">Save</button>
40.3.2 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식
이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티에 함수를 바인딩하면 이벤트 핸들러가 등록된다.
- 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티:
window객체,Document,HTMLElement타입의 DOM 노드 객체에 존재 - 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 키:
on접두사 + 이벤트 종류를 나타내는 이벤트 타입
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<button>Click me!</button>
<script>
const $button = document.querySelector('button');
// 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티에 이벤트 핸들러를 바인딩
$button.onclick = function () {
console.log('button click');
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
- 이벤트 타깃: 이벤트를 발생시킬 객체
- 예)
$button
- 예)
- 이벤트 타입: 이벤트의 종류
- 예)
onclick
- 예)
- 이벤트 핸들러: 이벤트 타깃 또는 전파된 이벤트를 캐치할 DOM 노드 객체에 바인딩
이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식 vs. 이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트 방식
- 이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트 방식은 결국 DOM 노드 객체의 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티로 변환되므로 결과적으로 동일한 방식
- 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식은 HTML과 자바스크립트가 섞이는 문제를 해결
- 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티에 하나의 이벤트 핸들러만 바인딩할 수 있다는 단점 존재
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<button>Click me!</button>
<script>
const $button = document.querySelector('button');
// 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식은 하나의 이벤트에 하나의 이벤트 핸들러만을 바인딩
// 첫 번째로 바인딩된 이벤트 핸들러는 두 번째 바인딩된 이벤트 핸들러에 의해 재할당되어
// 실행되지 않는다.
$button.onclick = function () {
console.log('Button clicked 1');
};
// 두 번째로 바인딩된 이벤트 핸들러
$button.onclick = function () {
console.log('Button clicked 2');
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
40.3.3 addEventListener 메서드 방식
EventTarget.prototype.addEventListener(eventType, functionName[, useCapture])- DOM Level 2에서 도입
- 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식과 이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트 방식은 DOM Level 0부터 제공
eventType: 이벤트의 종류를 나타내는 문자열on접두사를 붙이지 않는다.
functionName: 이벤트 핸들러useCapture: 이벤트를 캐치할 이벤트 전파 단계를 지정true: 캡처링 단계에서 이벤트를 캐치- 생략 또는
false: 버블링 단계에서 이벤트를 캐치
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<button>Click me!</button>
<script>
const $button = document.querySelector('button');
// 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식
// $button.onclick = function () {
// console.log('button click');
// };
// addEventListener 메서드 방식
$button.addEventListener('click', function () {
console.log('button click');
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
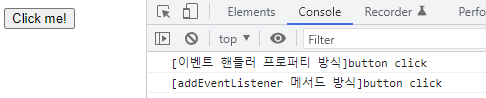
addEventListener메서드 방식은 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티에 바인딩된 이벤트 핸들러에 영향을 주지 않는다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <button>Click me!</button> <script> const $button = document.querySelector('button'); // 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식 $button.onclick = function () { console.log('[이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식]button click'); }; // addEventListener 메서드 방식 $button.addEventListener('click', function () { console.log('[addEventListener 메서드 방식]button click'); }); </script> </body> </html>
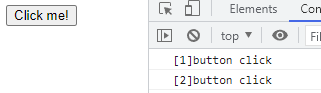
addEventListener메서드는 하나 이상의 이벤트 핸들러 등록 가능이벤트 핸들러는 등록된 순서대로 호출
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <button>Click me!</button> <script> const $button = document.querySelector('button'); // addEventListener 메서드는 동일한 요소에서 발생한 동일한 이벤트에 대해 // 하나 이상의 이벤트 핸들러를 등록할 수 있다. $button.addEventListener('click', function () { console.log('[1]button click'); }); $button.addEventListener('click', function () { console.log('[2]button click'); }); </script> </body> </html>
참조가 동일한 이벤트를 중복으로 등록하면 하나의 이벤트 핸들러만 등록
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <button>Click me!</button> <script> const $button = document.querySelector('button'); const handleClick = () => console.log('button click'); // 참조가 동일한 이벤트 핸들러를 중복 등록하면 하나의 핸들러만 등록된다. $button.addEventListener('click', handleClick); $button.addEventListener('click', handleClick); </script> </body> </html>
40.4 이벤트 핸들러 제거
Event.prototype.removeEventListener메서드addEventListener메서드와 동일한 인수를 전달해야 하며, 일치하지 않을 시 제거되지 않음1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <button>Click me!</button> <script> const $button = document.querySelector('button'); const handleClick = () => console.log('button click'); // 이벤트 핸들러 등록 $button.addEventListener('click', handleClick); // 이벤트 핸들러 제거 // addEventListener 메서드에 전달한 인수와 removeEventListener 메서드에 // 전달한 인수가 일치하지 않으면 이벤트 핸들러가 제거되지 않는다. $button.removeEventListener('click', handleClick, true); // 실패 $button.removeEventListener('click', handleClick); // 성공 </script> </body> </html>
- 무명 함수를 이벤트 핸들러로 등록한 경우 제거 불가
- 이벤트 핸들러의 참조를 변수나 자료구조에 저장하고 있어야 제거 가능
1 2 3
// 이벤트 핸들러 등록 $button.addEventListener('click', () => console.log('button click')); // 등록한 이벤트 핸들러를 참조할 수 없으므로 제거할 수 없다.
- 기명 이벤트 핸들러 내부에서 호출하여 제거하는 것은 가능
- 이벤트 핸들러는 한 번만 호출하게 된다.
1 2 3 4 5 6
// 기명 함수를 이벤트 핸들러로 등록 $button.addEventListener('click', function foo() { console.log('button click'); // 이벤트 핸들러를 제거한다. 따라서 이벤트 핸들러는 단 한 번만 호출된다. $button.removeEventListener('click', foo); });
- 기명 함수를 등록할 수 없다면 호출된 함수를 가리키는
arguments.callee사용 가능arguments.callee는 코드 최적화를 방해 → strict mode에서 사용 금지 ⇒ 이벤트 핸들러의 참조를 변수나 자료구조에 저장하는 것을 권장
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
// 무명 함수를 이벤트 핸들러로 등록 $button.addEventListener('click', function () { console.log('button click'); // 이벤트 핸들러를 제거한다. 따라서 이벤트 핸들러는 단 한 번만 호출된다. // arguments.callee는 호출된 함수, 즉 함수 자신을 가리킨다. $button.removeEventListener('click', arguments.callee); });
- 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식으로 등록한 이벤트 핸들러 제거
removeEventListener메서드 사용 불가- 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티에
null할당
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <button>Click me!</button> <script> const $button = document.querySelector('button'); const handleClick = () => console.log('button click'); // 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식으로 이벤트 핸들러 등록 $button.onclick = handleClick; // removeEventListener 메서드로 이벤트 핸들러를 제거할 수 없다. $button.removeEventListener('click', handleClick); // 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티에 null을 할당하여 이벤트 핸들러를 제거한다. $button.onclick = null; </script> </body> </html>
40.5 이벤트 객체
- 이벤트 발생 → 이벤트 객체가 동적으로 생성 → 이벤트 핸들러 첫 번째 인수로 전달
- 이벤트 객체: 이벤트에 대한 정보를 담고 있는 객체
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <p>클릭하세요. 클릭한 곳의 좌표가 표시됩니다.</p> <em class="message"></em> <script> const $msg = document.querySelector('.message'); // 클릭 이벤트에 의해 생성된 이벤트 객체는 이벤트 핸들러의 첫 번째 인수로 전달된다. function showCoords(e) { $msg.textContent = `clientX: ${e.clientX}, clientY: ${e.clientY}`; } document.onclick = showCoords; </script> </body> </html>
- 이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트 방식으로 등록한 경우
이벤트 객체를 전달받으려면 이벤트 핸들러 첫 번째 매개변수 이름이 반드시
event여야 한다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> html, body { height: 100%; } </style> </head> <!-- 이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트 방식의 경우 event가 아닌 다른 이름으로는 이벤트 객체를 전달받지 못한다. --> <body onclick="showCoords(event)"> <p>클릭하세요. 클릭한 곳의 좌표가 표시됩니다.</p> <em class="message"></em> <script> const $msg = document.querySelector('.message'); // 클릭 이벤트에 의해 생성된 이벤트 객체는 이벤트 핸들러의 첫 번째 인수로 전달 function showCoords(e) { $msg.textContent = `clientX: ${e.clientX}, clientY: ${e.clientY}`; } </script> </body> </html>
암묵적으로 생성되는 이벤트 핸들러의 함수 몸체에서 첫 번째 매개변수 이름이
event로 암묵적으로 명명되기 때문1 2 3 4 5
// onclick="showCoords(event)" 어트리뷰트는 파싱되어 // 다음 함수를 암묵적으로 생성한 뒤 onclick 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티에 할당한다. function onclick(event) { showCoords(event); }
40.5.1 이벤트 객체의 상속 구조
- 상속 구조
- Object
- Object
- Event
- AnimationEvent, UIEvent, ClipboardEvent, CustomEvent 등
- UIEvent
- UIEvent
- FocusEvent, MouseEvent, KeyboardEvent, InputEvent, TouchEvent 등
- MouseEvent
- MouseEvent
- DragEvent, WheelEvent
- Object
- 생성자 함수를 통한 이벤트 객체 생성
Event, UIEvent, MouseEvent 등 모두는 생성자 함수이므로 호출하여 이벤트 객체 생성 가능
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <script> // Event 생성자 함수를 호출하여 foo 이벤트 타입의 Event 객체를 생성한다. let e = new Event('foo'); console.log(e); // Event {isTrusted: false, type: "foo", target: null, ...} console.log(e.type); // "foo" console.log(e instanceof Event); // true console.log(e instanceof Object); // true // FocusEvent 생성자 함수를 호출하여 focus 이벤트 타입의 FocusEvent 객체를 생성 e = new FocusEvent('focus'); console.log(e); // FocusEvent {isTrusted: false, relatedTarget: null, view: null, ...} // MouseEvent 생성자 함수를 호출하여 click 이벤트 타입의 MouseEvent 객체를 생성 e = new MouseEvent('click'); console.log(e); // MouseEvent {isTrusted: false, screenX: 0, screenY: 0, clientX: 0, ... } // KeyboardEvent 생성자 함수를 호출하여 // keyup 이벤트 타입의 KeyboardEvent 객체를 생성한다. e = new KeyboardEvent('keyup'); console.log(e); // KeyboardEvent {isTrusted: false, key: "", code: "", ctrlKey: false, ...} // InputEvent 생성자 함수를 호출하여 // change 이벤트 타입의 InputEvent 객체를 생성 e = new InputEvent('change'); console.log(e); // InputEvent {isTrusted: false, data: null, inputType: "", ...} </script> </body> </html>
암묵적으로 생성되는 이벤트 객체도 생성자 함수가 생성한다.
- 생성된 이벤트 객체는 프로토타입 체인의 일원이 된다.
- Event 인터페이스
- DOM에서 발생한 이벤트에 의해 생성되는 이벤트 객체
- 모든 이벤트 객체의 공통 프로퍼티 정의
- FocusEvent, MouseEvent, KeyboardEvent, WheelEvent와 같은 하위 인터페이스는 이벤트 타입에 따른 고유한 프로퍼티 정의
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <input type="text"> <input type="checkbox"> <button>Click me!</button> <script> const $input = document.querySelector('input[type=text]'); const $checkbox = document.querySelector('input[type=checkbox]'); const $button = document.querySelector('button'); // load 이벤트가 발생하면 Event 타입의 이벤트 객체가 생성된다. window.onload = console.log; // change 이벤트가 발생하면 Event 타입의 이벤트 객체가 생성된다. $checkbox.onchange = console.log; // focus 이벤트가 발생하면 FocusEvent 타입의 이벤트 객체가 생성된다. $input.onfocus = console.log; // input 이벤트가 발생하면 InputEvent 타입의 이벤트 객체가 생성된다. $input.oninput = console.log; // keyup 이벤트가 발생하면 KeyboardEvent 타입의 이벤트 객체가 생성된다. $input.onkeyup = console.log; // click 이벤트가 발생하면 MouseEvent 타입의 이벤트 객체가 생성된다. $button.onclick = console.log; </script> </body> </html>
40.5.2 이벤트 객체의 공통 프로퍼티
- Event 인터페이스의 이벤트 관련 프로퍼티 = 모든 이벤트 객체가 상속받는 공통 프로퍼티
| 공통 프로퍼티 | 설명 | 타입 |
|---|---|---|
| type | 이벤트 타입 | string |
| target | 이벤트를 발생시킨 DOM 요소 | DOM 요소 |
| currentTarget | 이벤트 핸들러가 바인딩된 DOM 요소 | DOM 요소 노드 |
| eventPhase | 이벤트 전파 단계 0: 이벤트 없음 1: 캡처링 단계 2: 타깃 단계 3: 버블링 단계 | number |
| bubbles | 이벤트를 버블링으로 전파하는지 여부 포커스 이벤트(focus/blur), 리소스 이벤트(load, unload, abort, error), 마우스 이벤트(mouseenter, mouseleave)는 bubbles: false로 버블링하지 않는다. | boolean |
| cancelable | preventDefault 메서드를 호출하여 이벤트의 기본 동작을 취소할 수 있는지 여부 포커스 이벤트(focus/blur), 리소스 이벤트(load, unload, abort, error), 마우스 이벤트(mouseenter, mouseleave)는 cancelable: false로 취소할 수 없다. | boolean |
| defaultPrevented | preventDefault 메서드를 호출하여 이벤트를 취소했는지 여부 | boolean |
| isTrusted | 사용자의 행위에 의해 발생한 이벤트인지 여부 | boolean |
| timeStamp | 1970/01/01/00:00:0으로부터 이벤트 발생 시각까지 경과한 밀리초 | number |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<input type="checkbox">
<em class="message">off</em>
<script>
const $checkbox = document.querySelector('input[type=checkbox]');
const $msg = document.querySelector('.message');
// change 이벤트가 발생하면 Event 타입의 이벤트 객체가 생성된다.
$checkbox.onchange = e => {
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(e) === Event.prototype); // true
// e.target은 change 이벤트를 발생시킨 DOM 요소 $checkbox를 가리키고
// e.target.checked는 체크박스 요소의 현재 체크 상태를 나타낸다.
$msg.textContent = e.target.checked ? 'on' : 'off';
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
- 사용자 입력에 의해 체크박스 요소의 체크 상태 변경
checked프로퍼티 값 변경change이벤트 발생Event타입의 이벤트 객체 생성- 이벤트 객체의
target프로퍼티 →change이벤트를 발생시킨 DOM 요소$checkbox - 이벤트 객체의
currentTarget프로퍼티 → 이벤트 핸들러가 바인딩된 DOM 요소$checkbox
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
$checkbox.onchange = e => { // e.target은 change 이벤트를 발생시킨 DOM 요소 $checkbox를 가리키고 // e.currentTarget은 이벤트 핸들러가 바인딩된 DOM 요소 $checkbox를 가리킨다. console.log(e.target === e.currentTarget); // true $msg.textContent = e.target.checked ? 'on' : 'off'; };
- 이벤트 객체의
40.5.3 마우스 정보 취득
MouseEvent 타입의 이벤트 객체에서 마우스 정보를 취득할 수 있다.
click,dblclick,mousedown,mouseup,mousemove,mouseenter,mouseleave이벤트 발생 시 생성- 고유의 프로퍼티
- 마우스 포인터의 좌표 정보를 나타내는 프로퍼티
screenX/screenY,clientX/clientY,pageX/pageY,offsetX/offsetY
- 버튼 정보를 나타내는 프로퍼티
altKey,ctrlKey,shiftKey,button
- 마우스 포인터의 좌표 정보를 나타내는 프로퍼티
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.box {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #fff700;
border: 5px solid orange;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"></div>
<script>
// 드래그 대상 요소
const $box = document.querySelector('.box');
// 드래그 시작 시점의 마우스 포인터 위치
const initialMousePos = { x: 0, y: 0 };
// 오프셋: 이동할 거리
const offset = { x: 0, y: 0 };
// mousemove 이벤트 핸들러
const move = e => {
// 오프셋 = 현재(드래그하고 있는 시점) 마우스 포인터 위치
// - 드래그 시작 시점의 마우스 포인터 위치
offset.x = e.clientX - initialMousePos.x;
offset.y = e.clientY - initialMousePos.y;
// translate3d는 GPU를 사용하므로 absolute의 top, left를 사용하는 것보다 빠르다.
// top, left는 레이아웃에 영향을 준다.
$box.style.transform = `translate3d(${offset.x}px, ${offset.y}px, 0)`;
};
// mousedown 이벤트가 발생하면 드래그 시작 시점의 마우스 포인터 좌표를 저장한다.
$box.addEventListener('mousedown', e => {
// 이동 거리를 계산하기 위해 mousedown 이벤트가 발생(드래그를 시작)하면
// 드래그 시작 시점의 마우스 포인터 좌표(e.clientX/e.clientY: 뷰포트 상에서 현재
// 마우스의 포인터 좌표)를 저장해 둔다. 한번 이상 드래그로 이동한 경우 move에서
// translate3d(${offset.x}px, ${offset.y}px, 0)으로 이동한 상태이므로
// offset.x와 offset.y를 빼주어야 한다.
initialMousePos.x = e.clientX - offset.x;
initialMousePos.y = e.clientY - offset.y;
// mousedown 이벤트가 발생한 상태에서 mousemove 이벤트가 발생하면
// box 요소를 이동시킨다.
document.addEventListener('mousemove', move);
});
// mouseup 이벤트가 발생하면 mousemove 이벤트를 제거해 이동을 멈춘다.
document.addEventListener('mouseup', () => {
document.removeEventListener('mousemove', move);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
40.5.4 키보드 정보 취득
KeyboardEvent 타입의 이벤트 객체에서 키보드 정보를 취득할 수 있다.
keydown,keyup,keypress이벤트 발생 시 생성- 고유의 프로퍼티
ctrlKey,shiftKey,metaKey,key,keyCode(폐지)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<input type="text" />
<em class="message"></em>
<script>
const $input = document.querySelector('input[type=text]');
const $msg = document.querySelector('.message');
$input.onkeyup = e => {
// e.key는 입력한 키 값을 문자열로 반환한다.
// 입력한 키가 'Enter', 즉 엔터 키가 아니면 무시한다.
if (e.key !== 'Enter') return;
// 엔터키가 입력되면 현재까지 입력 필드에 입력된 값을 출력한다.
$msg.textContent = e.target.value;
e.target.value = '';
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
- 참고) 한글을 입력하고 엔터 키를 누르면
keyup이벤트 핸들러가 두 번 호출된다.- 이를 회피하려면
keyup대신keydown이벤트를 캐치한다.
- 이를 회피하려면
40.6 이벤트 전파
- DOM 트리 상에 존재하는 DOM 요소 노드에서 발생한 이벤트가 DOM 트리를 통해 전파되는 것
- 이벤트 발생 시 생성된 이벤트 객체는 이벤트를 발생시킨 DOM 요소인 이벤트 타깃을 중심으로 DOM 트리를 통해 전파된다.
- 캡처링 단계(capturing phase): 이벤트가 상위 요소에서 하위 요소로 방향으로 전파
- 타깃 단계(target phase): 이벤트가 타깃에 도달
- 버블링 단계(bubbling phase): 이벤트가 하위 요소에서 상위 요소 방향으로 전파
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<ul id="fruits">
<li id="apple">Apple</li>
<li id="banana">Banana</li>
<li id="orange">Orange</li>
</ul>
<script>
const $fruits = document.getElementById('fruits');
// #fruits 요소의 하위 요소인 li 요소를 클릭한 경우
$fruits.addEventListener('click', e => {
console.log(`이벤트 단계: ${e.eventPhase}`); // 3: 버블링 단계
console.log(`이벤트 타깃: ${e.target}`); // [object HTMLLIElement]
console.log(`커런트 타깃: ${e.currentTarget}`); // [object HTMLUListElement]
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
// 커런트 타깃은 ul 요소다.
li요소 클릭- 클릭 이벤트 발생
- 클릭 이벤트 객체 생성
- 이벤트 타깃 ⇒
li요소
- 이벤트 타깃 ⇒
- 클릭 이벤트 객체가
window에서 시작해 이벤트 타깃 방향으로 전파(캡처링 단계)- 이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트/프로퍼티 방식으로 등록한 이벤트 핸들러는 캡처링 단계의 이벤트를 캐치할 수 없다.
- 캡처링 단계의 이벤트를 캐치하려면
addEventListener메서드의 3번째 인수로true를 전달해야 한다.
- 이벤트 객체가 이벤트 타깃에 도착(타깃 단계)
- 이벤트를 발생시킨 이벤트 타깃과 이벤트 핸들러가 바인딩된 커런트 타깃이 같은 DOM 요소인 경우 타깃 단계의 이벤트를 캐치한다.
- 이벤트 객체가 이벤트 타깃에서
window방향으로 전파(버블링 단계)- 위 예제는 버블링 단계의 이벤트를 캐치한다.
이벤트 캐치
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<ul id="fruits">
<li id="apple">Apple</li>
<li id="banana">Banana</li>
<li id="orange">Orange</li>
</ul>
<script>
const $fruits = document.getElementById('fruits');
const $banana = document.getElementById('banana');
// #fruits 요소의 하위 요소인 li 요소를 클릭한 경우
// 캡처링 단계의 이벤트를 캐치한다.
$fruits.addEventListener('click', e => {
console.log(`이벤트 단계: ${e.eventPhase}`); // 1: 캡처링 단계
console.log(`이벤트 타깃: ${e.target}`); // [object HTMLLIElement]
console.log(`커런트 타깃: ${e.currentTarget}`); // [object HTMLUListElement]
}, true);
// 타깃 단계의 이벤트를 캐치한다.
$banana.addEventListener('click', e => {
console.log(`이벤트 단계: ${e.eventPhase}`); // 2: 타깃 단계
console.log(`이벤트 타깃: ${e.target}`); // [object HTMLLIElement]
console.log(`커런트 타깃: ${e.currentTarget}`); // [object HTMLLIElement]
});
// 버블링 단계의 이벤트를 캐치한다.
$fruits.addEventListener('click', e => {
console.log(`이벤트 단계: ${e.eventPhase}`); // 3: 버블링 단계
console.log(`이벤트 타깃: ${e.target}`); // [object HTMLLIElement]
console.log(`커런트 타깃: ${e.currentTarget}`); // [object HTMLUListElement]
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
DOM 트리를 통해 전파되는 이벤트는 이벤트 패스에 위치한 모든 DOM 요소에서 캐치할 수 있다.
- 이벤트 패스: 이벤트가 통과하는 DOM 프리상의 경로
Event.prototype.composedPath메서드로 확인 가능
이벤트 버블링 예외
- 대부분의 이벤트는 캡처링/버블링을 통해 전파되지만, 버블링을 통해 전파되지 않는 이벤트 존재
- 포커스 이벤트(focus/blur)
- 리소스 이벤트(load, unload, abort, error)
- 마우스 이벤트(mouseenter, mouseleave)
event.bubbles값으로false를 가진다.
- 이벤트 타깃 상위 요소에서 이를 캐치하려면 캡처링 단계의 이벤트를 캐치해야 한다.
- 이러한 경우는 흔하지 않으며 대체할 수 있는 이벤트가 존재해 버블링 단계에서 캐치할 수 있다.
- focus/blur → focusin/focusout
- mouseenter, mouseleave → mouseover/mouseout
- 이러한 경우는 흔하지 않으며 대체할 수 있는 이벤트가 존재해 버블링 단계에서 캐치할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
html, body { height: 100%; }
</style>
<body>
<p>버블링과 캡처링 이벤트 <button>버튼</button></p>
<script>
// 버블링 단계의 이벤트를 캐치
document.body.addEventListener('click', () => {
console.log('Handler for body.');
});
// 캡처링 단계의 이벤트를 캐치
document.querySelector('p').addEventListener('click', () => {
console.log('Handler for paragraph.');
}, true);
// 타깃 단계의 이벤트를 캐치
document.querySelector('button').addEventListener('click', () => {
console.log('Handler for button.');
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
button요소에서 클릭 이벤트 발생1 2 3
Handler for paragraph. Handler for button. Handler for body.
p요소에서 클릭 이벤트 발생1 2
Handler for paragraph. Handler for body.
40.7 이벤트 위임
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#fruits {
display: flex;
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
}
#fruits li {
width: 100px;
cursor: pointer;
}
#fruits .active {
color: red;
text-decoration: underline;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<nav>
<ul id="fruits">
<li id="apple" class="active">Apple</li>
<li id="banana">Banana</li>
<li id="orange">Orange</li>
</ul>
</nav>
<div>선택된 내비게이션 아이템: <em class="msg">apple</em></div>
<script>
const $fruits = document.getElementById('fruits');
const $msg = document.querySelector('.msg');
// 사용자 클릭에 의해 선택된 내비게이션 아이템(li 요소)에 active 클래스를 추가하고
// 그 외의 모든 내비게이션 아이템의 active 클래스를 제거한다.
function activate({ target }) {
[...$fruits.children].forEach($fruit => {
$fruit.classList.toggle('active', $fruit === target);
$msg.textContent = target.id;
});
}
// 모든 내비게이션 아이템(li 요소)에 이벤트 핸들러를 등록한다.
document.getElementById('apple').onclick = activate;
document.getElementById('banana').onclick = activate;
document.getElementById('orange').onclick = activate;
</script>
</body>
</html>
- 문제) DOM 요소마다 이벤트 핸들로 등록
- 성능 저하의 원인
- 유지 보수에 부적합
- 해결) 이벤트 위임(event delegation) 이용
- 이벤트 위임: 여러 개의 하위 DOM 요소에 각각 이벤트 핸들러를 등록하는 대신 하나의 상위 DOM 요소에 이벤트 핸들러를 등록하는 방법
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> #fruits { display: flex; list-style-type: none; padding: 0; } #fruits li { width: 100px; cursor: pointer; } #fruits .active { color: red; text-decoration: underline; } </style> </head> <body> <nav> <ul id="fruits"> <li id="apple" class="active">Apple</li> <li id="banana">Banana</li> <li id="orange">Orange</li> </ul> </nav> <div>선택된 내비게이션 아이템: <em class="msg">apple</em></div> <script> const $fruits = document.getElementById('fruits'); const $msg = document.querySelector('.msg'); // 사용자 클릭에 의해 선택된 내비게이션 아이템(li 요소)에 active 클래스를 추가하고 // 그 외의 모든 내비게이션 아이템의 active 클래스를 제거한다. function activate({ target }) { // 이벤트를 발생시킨 요소(target)가 ul#fruits의 자식 요소가 아니라면 무시한다. if (!target.matches('#fruits > li')) return; [...$fruits.children].forEach($fruit => { $fruit.classList.toggle('active', $fruit === target); $msg.textContent = target.id; }); } // 이벤트 위임: 상위 요소(ul#fruits)는 하위 요소의 이벤트를 캐치할 수 있다. $fruits.onclick = activate; </script> </body> </html>
- 이벤트 위임 주의사항
- 이벤트를 실제로 발생시킨 DOM 요소가 기대한 DOM 요소가 아닐 수 있다.
- 따라서 필요한 DOM 요소에 한정해 이벤트 핸들러가 실행되도록 이벤트 타깃을 검사해야 한다.
Element.prototype.matches메서드는 인수로 전달된 선택자에 의해 특정 노드를 탐색 가능한지 확인1 2 3 4
function activate({ target }) { // 이벤트를 발생시킨 요소(target)이 ul#fruits의 자식 요소가 아니라면 무시한다. if (!target.matches('#fruits > li')) return; ...
- 또한 이벤트를 위임하면 이벤트 객체의
target프로퍼티와currentTarget프로퍼티가 다른 DOM 요소를 가리킬 수 있다.
40.8 DOM 요소의 기본 동작 조작
40.8.1 DOM 요소의 기본 동작 중단
- 이벤트 객체의
preventDefault메서드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<a href="https://www.google.com">go</a>
<input type="checkbox">
<script>
document.querySelector('a').onclick = e => {
// a 요소의 기본 동작을 중단한다.
e.preventDefault();
};
document.querySelector('input[type=checkbox]').onclick = e => {
// checkbox 요소의 기본 동작을 중단한다.
e.preventDefault();
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
// a 요소를 클릭하면 href 어트리뷰트에 지정된 링크로 이동한다.
// checkbox 또는 raio 요소는 클릭하면 체크 또는 해제된다.
40.8.2 이벤트 전파 방지
- 이벤트 객체의
stopPropagation메서드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div class="container">
<button class="btn1">Button 1</button>
<button class="btn2">Button 2</button>
<button class="btn3">Button 3</button>
</div>
<script>
// 이벤트 위임. 클릭된 하위 버튼 요소의 color를 변경한다.
document.querySelector('.container').onclick = ({ target }) => {
if (!target.matches('.container > button')) return;
target.style.color = 'red';
};
// .btn2 요소는 이벤트를 전파하지 않으므로 상위 요소에서 이벤트를 캐치할 수 없다.
document.querySelector('.btn2').onclick = e => {
e.stopPropagation(); // 이벤트 전파 중단
e.target.style.color = 'blue';
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
40.9 이벤트 핸들러 내부의 this
40.9.1 이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트 방식
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<button onclick="handleClick()">Click me</button>
<script>
function handleClick() {
console.log(this); // window
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
- 이벤트 핸들러 어트리뷰트의 값에 지정된 문자열
⇒ 암묵적으로 생성되는 이벤트 핸들러의 문
⇒handleClick함수는 이벤트 핸들러에 의해 일반 함수로 호출
⇒ 일반 함수로서 호출된 함수 내부의this는 전역 객체를 가리킴
⇒window를 가리킨다. 이벤트 핸들러를 호출할 때 인수로 전달한
this⇒ 이벤트를 바인딩한 DOM 요소1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <button onclick="handleClick(this)">Click me</button> <script> function handleClick(button) { console.log(button); // 이벤트를 바인딩한 button 요소 console.log(this); // window } </script> </body> </html>
handleClick함수에 전달한this
⇒ 암묵적으로 생성된 이벤트 핸들러 내부의this
⇒ 이벤트를 바인딩한 DOM 요소
40.9.2 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식과 addEventListener 메서드 방식
이벤트 핸들러 내부의
this⇒ 이벤트를 바인딩한 DOM 요소 =currentTarget프로퍼티1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <button class="btn1">0</button> <button class="btn2">0</button> <script> const $button1 = document.querySelector('.btn1'); const $button2 = document.querySelector('.btn2'); // 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식 $button1.onclick = function (e) { // this는 이벤트를 바인딩한 DOM 요소를 가리킨다. console.log(this); // $button1 console.log(e.currentTarget); // $button1 console.log(this === e.currentTarget); // true // $button1의 textContent를 1 증가시킨다. ++this.textContent; }; // addEventListener 메서드 방식 $button2.addEventListener('click', function (e) { // this는 이벤트를 바인딩한 DOM 요소를 가리킨다. console.log(this); // $button2 console.log(e.currentTarget); // $button2 console.log(this === e.currentTarget); // true // $button2의 textContent를 1 증가시킨다. ++this.textContent; }); </script> </body> </html>
화살표 함수로 정의한 이벤트 핸들러 내부의
this⇒ 상위 스코프의this1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <button class="btn1">0</button> <button class="btn2">0</button> <script> const $button1 = document.querySelector('.btn1'); const $button2 = document.querySelector('.btn2'); // 이벤트 핸들러 프로퍼티 방식 $button1.onclick = e => { // 화살표 함수 내부의 this는 상위 스코프의 this를 가리킨다. console.log(this); // window console.log(e.currentTarget); // $button1 console.log(this === e.currentTarget); // false // this는 window를 가리키므로 window.textContent에 NaN(undefined + 1)을 할당 ++this.textContent; }; // addEventListener 메서드 방식 $button2.addEventListener('click', e => { // 화살표 함수 내부의 this는 상위 스코프의 this를 가리킨다. console.log(this); // window console.log(e.currentTarget); // $button2 console.log(this === e.currentTarget); // false // this는 window를 가리키므로 window.textContent에 NaN(undefined + 1)을 할당 ++this.textContent; }); </script> </body> </html>
클래스에서 이벤트 핸들러를 바인딩하는 경우
- 이벤트 핸들러 내부의
this≠ 클래스가 생성할 인스턴스 이벤트 핸들러 내부의
this⇒ 이벤트를 바인딩한 DOM 요소1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <button class="btn">0</button> <script> class App { constructor() { this.$button = document.querySelector('.btn'); this.count = 0; // increase 메서드를 이벤트 핸들러로 등록 this.$button.onclick = this.increase; } increase() { // 이벤트 핸들러 increase 내부의 this는 DOM 요소(this.$button)를 가리킨다. // 따라서 this.$button은 this.$button.$button과 같다. this.$button.textContent = ++this.count; // -> TypeError: Cannot set property 'textContent' of undefined } } new App(); </script> </body> </html>
bind메서드를 사용해this를 전달해야 메서드 내부this가 클래스가 생성할 인스턴스를 가리킨다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <button class="btn">0</button> <script> class App { constructor() { this.$button = document.querySelector('.btn'); this.count = 0; // increase 메서드를 이벤트 핸들러로 등록 // this.$button.onclick = this.increase; // increase 메서드 내부의 this가 인스턴스를 가리키도록 한다. this.$button.onclick = this.increase.bind(this); } increase() { this.$button.textContent = ++this.count; } } new App(); </script> </body> </html>
- 또는 클래스 필드에 할당한 화살표 함수를 이벤트 핸들러로 등록해도
this가 인스턴스를 가리킨다.- 이때 이벤트 핸들러는 프로토타입 메서드가 아닌 인스턴스 메서드가 된다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <button class="btn">0</button> <script> class App { constructor() { this.$button = document.querySelector('.btn'); this.count = 0; // 화살표 함수인 increase를 이벤트 핸들러로 등록 this.$button.onclick = this.increase; } // 클래스 필드 정의 // increase는 인스턴스 메서드이며 내부의 this는 인스턴스를 가리킨다. increase = () => this.$button.textContent = ++this.count; } new App(); </script> </body> </html>
- 이벤트 핸들러 내부의
40.10 이벤트 핸들러에 인수 전달
이벤트 핸들러 내부에서 함수를 호출하며 인수 전달 가능
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <label>User name <input type='text'></label> <em class="message"></em> <script> const MIN_USER_NAME_LENGTH = 5; // 이름 최소 길이 const $input = document.querySelector('input[type=text]'); const $msg = document.querySelector('.message'); const checkUserNameLength = min => { $msg.textContent = $input.value.length < min ? `이름은 ${min}자 이상 입력해 주세요` : ''; }; // 이벤트 핸들러 내부에서 함수를 호출하면서 인수를 전달한다. $input.onblur = () => { checkUserNameLength(MIN_USER_NAME_LENGTH); }; </script> </body> </html>
이벤트 핸들러를 반환하는 함수를 호출하며 인수 전달 가능
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <label>User name <input type='text'></label> <em class="message"></em> <script> const MIN_USER_NAME_LENGTH = 5; // 이름 최소 길이 const $input = document.querySelector('input[type=text]'); const $msg = document.querySelector('.message'); // 이벤트 핸들러를 반환하는 함수 const checkUserNameLength = min => e => { $msg.textContent = $input.value.length < min ? `이름은 ${min}자 이상 입력해 주세요` : ''; }; // 이벤트 핸들러를 반환하는 함수를 호출하면서 인수를 전달한다. $input.onblur = checkUserNameLength(MIN_USER_NAME_LENGTH); </script> </body> </html>
40.11 커스텀 이벤트
40.11.1 커스텀 이벤트 생성
Event,UIEvent,MouseEvent같은 이벤트 생성자 함수를 호출해 명시적으로 생성한 이벤트 객체는 임의의 이벤트 타입 지정 가능- 이벤트 생성자 함수로 커스텀 이벤트 생성
- 첫 번째 인수: 이벤트 타입을 나타내는 문자열
- 기존 이벤트 타입이 아닌 임의의 문자열을 사용할 경우 일반적으로
CustomEvent이벤트 생성자 함수 사용
- 기존 이벤트 타입이 아닌 임의의 문자열을 사용할 경우 일반적으로
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
// KeyboardEvent 생성자 함수로 keyup 이벤트 타입의 커스텀 이벤트 객체를 생성 const keyboardEvent = new KeyboardEvent('keyup'); console.log(keyboardEvent.type); // keyup // CustomEvent 생성자 함수로 foo 이벤트 타입의 커스텀 이벤트 객체를 생성 const customEvent = new CustomEvent('foo'); console.log(customEvent.type); // foo
- 첫 번째 인수: 이벤트 타입을 나타내는 문자열
- 커스텀 이벤트 객체
bubbles프로퍼티 값이false로 기본 설정 ⇒ 버블링되지 않는다.cancelable프로퍼티 값이false로 기본 설정 ⇒preventDefault메서드로 취소 불가
1 2 3 4 5
// MouseEvent 생성자 함수로 click 이벤트 타입의 커스텀 이벤트 객체를 생성 const customEvent = new MouseEvent('click'); console.log(customEvent.type); // click console.log(customEvent.bubbles); // false console.log(customEvent.cancelable); // false
생성자 함수 두 번째 인수로
bubbles또는cancelable프로퍼티를 갖는 객체를 전달해 이를true로 설정 가능1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
// MouseEvent 생성자 함수로 click 이벤트 타입의 커스텀 이벤트 객체를 생성 const customEvent = new MouseEvent('click', { bubbles: true, cancelable: true }); console.log(customEvent.bubbles); // true console.log(customEvent.cancelable); // true
그 외 이벤트 타입에 따른 고유 프로퍼티 값도 지정 가능
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
// MouseEvent 생성자 함수로 click 이벤트 타입의 커스텀 이벤트 객체를 생성 const mouseEvent = new MouseEvent('click', { bubbles: true, cancelable: true, clientX: 50, clientY: 100 }); console.log(mouseEvent.clientX); // 50 console.log(mouseEvent.clientY); // 100 // KeyboardEvent 생성자 함수로 keyup 이벤트 타입의 커스텀 이벤트 객체를 생성 const keyboardEvent = new KeyboardEvent('keyup', { key: 'Enter' }); console.log(keyboardEvent.key); // Enter
- 이벤트 생성자 함수로 생성된 커스텀 이벤트는
isTrusted프로퍼티 값이 언제나false- 사용자의 행위로 인해 발생한 이벤트에 의해 생성된 이벤트 객체는 언제나
true
1 2 3
// InputEvent 생성자 함수로 foo 이벤트 타입의 커스텀 이벤트 객체를 생성 const customEvent = new InputEvent('foo'); console.log(customEvent.isTrusted); // false
- 사용자의 행위로 인해 발생한 이벤트에 의해 생성된 이벤트 객체는 언제나
40.11.2 커스텀 이벤트 디스패치
- 커스텀 이벤트는
dispatchEvent메서드로 디스패치(이벤트를 발생시키는 행위) 가능 dispatchEvent메서드- 인수로 이벤트 객체를 전달하며 호출 → 전달된 이벤트 타입의 이벤트가 발생
- 이벤트 핸들러를 동기 처리 방식으로 호출
- 따라서 디스패치 이전에 커스텀 이벤트를 처리할 이벤트 핸들러를 등록해야 한다.
- 일반적으로 이벤트 핸들러는 비동기 처리 방식으로 동작
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <button class="btn">Click me</button> <script> const $button = document.querySelector('.btn'); // 버튼 요소에 click 커스텀 이벤트 핸들러를 등록 // 커스텀 이벤트를 디스패치하기 이전에 이벤트 핸들러를 등록해야 한다. $button.addEventListener('click', e => { console.log(e); // MouseEvent {isTrusted: false, screenX: 0, ...} alert(`${e} Clicked!`); }); // 커스텀 이벤트 생성 const customEvent = new MouseEvent('click'); // 커스텀 이벤트 디스패치(동기 처리). click 이벤트가 발생한다. $button.dispatchEvent(customEvent); </script> </body> </html>
CustomEvent이벤트 생성자 함수- 두 번째 인수: 이벤트와 함께 전달하고 싶은 정보를 담은
detail프로퍼티를 포함하는 객체- 이 정보는 이벤트 객체의
detail프로퍼티에 담겨 전달
- 이 정보는 이벤트 객체의
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <button class="btn">Click me</button> <script> const $button = document.querySelector('.btn'); // 버튼 요소에 foo 커스텀 이벤트 핸들러를 등록 // 커스텀 이벤트를 디스패치하기 이전에 이벤트 핸들러를 등록해야 한다. $button.addEventListener('foo', e => { // e.detail에는 CustomEvent 함수의 두 번째 인수로 전달한 정보가 담겨 있다. alert(e.detail.message); }); // CustomEvent 생성자 함수로 foo 이벤트 타입의 커스텀 이벤트 객체를 생성 const customEvent = new CustomEvent('foo', { detail: { message: 'Hello' } // 이벤트와 함께 전달하고 싶은 정보 }); // 커스텀 이벤트 디스패치 $button.dispatchEvent(customEvent); </script> </body> </html>
- 두 번째 인수: 이벤트와 함께 전달하고 싶은 정보를 담은
- 임의의 이벤트 타입을 지정해 커스텀 이벤트 객체를 생성한 경우 반드시
addEventListener메서드 방식으로 이벤트 핸들러 등록on + 이벤트 타입으로 이루어진 이벤트 핸들로 어트리뷰트/프로퍼티가 요소 노드에 존재하지 않기 때문에 등록 불가