[모던 자바스크립트 Deep Dive]45장 프로미스
45.1 비동기 처리를 위한 콜백 패턴의 단점
45.1.1 콜백 헬
- 비동기 함수: 함수 내부에 비동기로 동작하는 코드를 포함한 함수
- 호출 시 비동기로 동작하는 코드가 완료되지 않아도 기다리지 않고 종료
- 비동기로 동작하는 코드의 처리 결과를 이용하기 어려움
1 2 3 4 5 6
let g = 0; // 비동기 함수인 setTimeout 함수는 콜백 함수의 처리 결과를 외부로 반환하거나 // 상위 스코프의 변수에 할당하지 못한다. setTimeout(() => { g = 100; }, 0); console.log(g); // 0
비동기 함수의 문제
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
// GET 요청을 위한 비동기 함수 const get = url => { const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); xhr.open('GET', url); xhr.send(); xhr.onload = () => { if (xhr.status === 200) { // 서버의 응답을 콘솔에 출력한다. console.log(JSON.parse(xhr.response)); } else { console.error(`${xhr.status} ${xhr.statusText}`); } }; }; // id가 1인 post를 취득 get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1'); /* { "userId": 1, "id": 1, "title": "sunt aut facere ...", "body": "quia et suscipit ..." } */
onload이벤트 핸들러는 비동기로 동작하기 때문에get함수 종료 이후 실행 ⇒ 서버의 응답 결과를 반환하거나 상위 스코프 변수에 할당할 수 없다.onload이벤트 핸들러의 반환값은 캐치할 수도 없다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
// GET 요청을 위한 비동기 함수 const get = url => { const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); xhr.open('GET', url); xhr.send(); xhr.onload = () => { if (xhr.status === 200) { // ① 서버의 응답을 반환한다. return JSON.parse(xhr.response); } console.error(`${xhr.status} ${xhr.statusText}`); }; }; // ② id가 1인 post를 취득 const response = get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1'); console.log(response); // undefined
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <input type="text"> <script> document.querySelector('input').oninput = function () { console.log(this.value); // 이벤트 핸들러에서의 반환은 의미가 없다. return this.value; }; </script> </body> </html>
상위 스코프 변수에 할당도 어렵다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
let todos; // GET 요청을 위한 비동기 함수 const get = url => { const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); xhr.open('GET', url); xhr.send(); xhr.onload = () => { if (xhr.status === 200) { // ① 서버의 응답을 상위 스코프의 변수에 할당한다. todos = JSON.parse(xhr.response); } else { console.error(`${xhr.status} ${xhr.statusText}`); } }; }; // id가 1인 post를 취득 get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1'); console.log(todos); // ② undefined
- 이벤트 핸들러가 실행되는 시점에는 콜 스택이 비어있어야 하므로 절대
console.log전에 실행되지 않는다.xhr.onload이벤트 핸들러는load이벤트 발생 시 태스크 큐에 저장되어 대기- 콜 스택이 비면 이벤트 루프에 의해 콜스택으로 푸시되어 실행
- 이후 이벤트 핸들러의 평가 → 이벤트 핸들러의 실행 컨텍스트 생성 → 콜 스택에 푸시 → 이벤트 핸들러 실행 과정 진행
비동기 함수의 결과는 비동기 함수 내부에서 처리한다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
// GET 요청을 위한 비동기 함수 const get = (url, successCallback, failureCallback) => { const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); xhr.open('GET', url); xhr.send(); xhr.onload = () => { if (xhr.status === 200) { // 서버의 응답을 콜백 함수에 인수로 전달하면서 호출하여 응답에 대한 후속 처리 진행 successCallback(JSON.parse(xhr.response)); } else { // 에러 정보를 콜백 함수에 인수로 전달하면서 호출하여 에러 처리를 한다. failureCallback(xhr.status); } }; }; // id가 1인 post를 취득 // 서버의 응답에 대한 후속 처리를 위한 콜백 함수를 비동기 함수인 get에 전달해야 한다. get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1', console.log, console.error); /* { "userId": 1, "id": 1, "title": "sunt aut facere ...", "body": "quia et suscipit ..." } */
하지만 콜백 함수 호출이 중첩된다면 콜벡 헬이 발생한다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
// GET 요청을 위한 비동기 함수 const get = (url, callback) => { const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); xhr.open('GET', url); xhr.send(); xhr.onload = () => { if (xhr.status === 200) { // 서버의 응답을 콜백 함수에 전달하면서 호출하여 응답에 대한 후속 처리 진행 callback(JSON.parse(xhr.response)); } else { console.error(`${xhr.status} ${xhr.statusText}`); } }; }; const url = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com'; // id가 1인 post의 userId를 취득 get(`${url}/posts/1`, ({ userId }) => { console.log(userId); // 1 // post의 userId를 사용하여 user 정보를 취득 get(`${url}/users/${userId}`, userInfo => { console.log(userInfo); // {id: 1, name: "Leanne Graham", username: "Bret",...} }); });
- 콜백 헬
- 콜백 함수 호출이 중첩되어 복잡도가 높아지는 현상
- 가독성을 나쁘게 하며 실수를 유발하는 원인이 된다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
get('/step1', a => { get(`/step2/${a}`, b => { get(`/step3/${b}`, c => { get(`/step4/${c}`, d => { console.log(d); }); }); }); });
45.1.2 에러 처리의 한계
1
2
3
4
5
6
try {
setTimeout(() => { throw new Error('Error!'); }, 1000);
} catch (e) {
// 에러를 캐치하지 못한다
console.error('캐치한 에러', e);
}
- 에러는 호출자(caller) 방향으로 전파된다.
- 하지만
setTimeout함수의 콜백 함수를 호출한 건setTimeout함수가 아니다.setTimeout함수는 콜백 함수가 실행될 때 이미 콜 스택에서 제거된 상태다.
- 따라서 에러는
catch블록에서 캐치되지 않는다.
45.2 프로미스의 생성
- 프로미스
- 비동기 처리를 위한 콜백 패턴의 콜백 헬과 에러 처리가 곤란한 문제를 극복하기 위해 ES6에서 도입
- ECMAScript 사양에 정의된 표준 빌트인 객체
- 비동기 처리 상태와 처리 결과를 관리하는 객체
Promise생성자 함수new연산자와 함께 호출하면 프로미스(Promise객체) 생성- 인수: 비동기 처리를 수행할 콜백 함수
- ECMAScript 사양에서 executor 함수라 부른다.
- 콜백 함수 내부에서 비동기 처리 수행
resolve,reject함수를 인수로 전달받는다.- 비동기 처리 성공 →
resolve함수 호출 - 비동기 처리 실패 →
reject함수 호출
- 비동기 처리 성공 →
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
// 프로미스 생성 const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { // Promise 함수의 콜백 함수 내부에서 비동기 처리를 수행한다. if (/* 비동기 처리 성공 */) { resolve('result'); } else { /* 비동기 처리 실패 */ reject('failure reason'); } });
비동기 함수 → 프로미스
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
// GET 요청을 위한 비동기 함수 const promiseGet = url => { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); xhr.open('GET', url); xhr.send(); xhr.onload = () => { if (xhr.status === 200) { // 성공적으로 응답을 전달받으면 resolve 함수를 호출한다. resolve(JSON.parse(xhr.response)); } else { // 에러 처리를 위해 reject 함수를 호출한다. reject(new Error(xhr.status)); } }; }); }; // promiseGet 함수는 프로미스를 반환한다. promiseGet('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1');
- 프로미스 비동기 처리 상태 정보
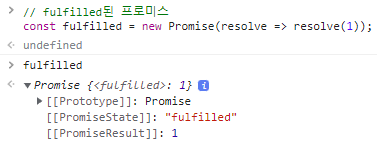
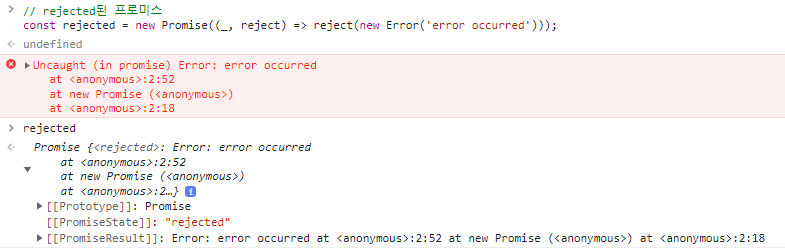
프로미스의 비동기 처리 상태 정보는 프로미스의 내부 슬롯
[[PromiseStatus]]에 저장되며, 접근할 수는 없다.비동기 처리 상태 정보 의미 상태 변경 조건 pending 비동기 처리가 아직 수행되지 않은 상태 프로미스가 생성된 직후 기본 상태 fulfilled 비동기 처리가 수행된 상태(성공) resolve 함수 호출 rejected 비동기 처리가 수행된 상태(실패) reject 함수 호출 - 비동기 처리 성공 →
resolve함수 호출 → 프로미스 상태를fulfilled로 변경 - 비동기 처리 실패 →
reject함수 호출 → 프로미스 상태를rejected로 변경 settled상태:fulfilled또는rejected상태pending이 아닌 상태- 비동기 처리가 수행된 상태
- 더 이상 다른 상태로 변화 불가
- 프로미스의 비동기 처리 결과 정보
- 프로미스는 비동기 처리 결과도 상태로 갖는다.
1 2
// fulfilled된 프로미스 const fulfilled = new Promise(resolve => resolve(1));
1 2
// rejected된 프로미스 const rejected = new Promise((_, reject) => reject(new Error('error occurred')));
45.3 프로미스의 후속 처리 메서드
- 프로미스의 비동기 처리 상태 변화
- 후속 처리 메서드에 인수로 전달한 콜백 함수를 선택적으로 호출
- 콜백 함수에 프로미스의 처리 결과를 인수로 전달
- 후속 처리 메서드는 비동기로 동작 → 프로미스 반환
45.3.1 Promise.prototype.then
then메서드- 언제나 프로미스 반환
then메서드의 콜백 함수가 프로미스를 반환하면 그 프로미스를 그대로 반환- 콜백 함수가 프로미스를 반환하지 않으면 반환 값을 암묵적으로
resolve또는reject하여 프로미스를 생성해 반환
- 언제나 프로미스 반환
then메서드가 인수로 하는 두 콜백 함수- 첫 번째 콜백 함수: 프로미스가
fulfilled상태가 되면 호출- 즉 비동기 처리 성공 시 호출
- 프로미스의 비동기 처리 결과를 인수로 전달받는다.
- 두 번째 콜백 함수: 프로미스가
rejected상태가 되면 호출- 즉 비동기 처리 실패 시 호출
- 프로미스의 비동기 처리 결과를 인수로 전달받는다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
// fulfilled new Promise(resolve => resolve('fulfilled')) .then(v => console.log(v), e => console.error(e)); // fulfilled // rejected new Promise((_, reject) => reject(new Error('rejected'))) .then(v => console.log(v), e => console.error(e)); // Error: rejected
- 첫 번째 콜백 함수: 프로미스가
45.3.2 Promise.prototype.catch
catch메서드then(undefined, onRejected)와 동일하게 작동 ⇒then메서드처럼 언제나 프로미스 반환
1 2 3
// rejected new Promise((_, reject) => reject(new Error('rejected'))) .then(undefined, e => console.log(e)); // Error: rejected
catch메서드는 인수로 하나의 콜백 함수를 받는다.- 프로미스가
rejected상태인 경우에만 호출
1 2 3
// rejected new Promise((_, reject) => reject(new Error('rejected'))) .catch(e => console.log(e)); // Error: rejected
- 프로미스가
45.3.3 Promise.prototype.finally
finally메서드- 언제나 프로미스 반환
finally메서드는 인수로 하나의 콜백 함수를 받는다.- 프로미스의 성공 또는 실패와 상관없이 무조건 한 번 호출된다.
- 프로미스 상태와 무관하게 공통으로 수행할 처리 내용에 유용하게 쓸 수 있다.
1 2
new Promise(() => {}) .finally(() => console.log('finally')); // finally
프로미스로 구현한 비동기 함수와 후속 처리
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
const promiseGet = url => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET', url);
xhr.send();
xhr.onload = () => {
if (xhr.status === 200) {
// 성공적으로 응답을 전달받으면 resolve 함수를 호출한다.
resolve(JSON.parse(xhr.response));
} else {
// 에러 처리를 위해 reject 함수를 호출한다.
reject(new Error(xhr.status));
}
};
});
};
// promiseGet 함수는 프로미스를 반환한다.
promiseGet('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1')
.then(res => console.log(res))
.catch(err => console.error(err))
.finally(() => console.log('Bye!'));
45.4 프로미스의 에러 처리
프로미스는 비동기 함수와 달리 문제없이 에러를 처리할 수 있다.
then메서드의 두 번째 콜백 함수로 처리1 2 3 4 5 6 7
const wrongUrl = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/XXX/1'; // 부적절한 URL이 지정되었기 때문에 에러가 발생한다. promiseGet(wrongUrl).then( res => console.log(res), err => console.error(err) ); // Error: 404
두 번째 콜백 함수는 첫 번째 콜백 함수의 에러를 캐치 못하고, 코드를 복잡하게 해 가독성을 떨어뜨린다.
1 2 3 4
promiseGet('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1').then( res => console.xxx(res), err => console.error(err) ); // 두 번째 콜백 함수는 첫 번째 콜백 함수에서 발생한 에러를 캐치하지 못한다.
catch메서드를 사용해 처리1 2 3 4 5 6
const wrongUrl = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/XXX/1'; // 부적절한 URL이 지정되었기 때문에 에러가 발생한다. promiseGet(wrongUrl) .then(res => console.log(res)) .catch(err => console.error(err)); // Error: 404
[catch메서드는 내부적으로then(undefined, onRejected)을 호출한다.](https://262.ecma-international.org/11.0/#sec-promise.prototype.catch)1 2 3 4 5 6
const wrongUrl = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/XXX/1'; // 부적절한 URL이 지정되었기 때문에 에러가 발생한다. promiseGet(wrongUrl) .then(res => console.log(res)) .then(undefined, err => console.error(err)); // Error: 404
비동기 처리뿐만 아니라
then메서드 내부에서 발생한 에러도 캐치할 수 있다.- 또한
then메서드의 두 번째 콜백 함수를 사용하는 것보다 가독성이 좋고 명확하다. - 따라서 예외 처리는
catch메서드를 사용하는 걸 권장한다.
1 2 3
promiseGet('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1') .then(res => console.xxx(res)) .catch(err => console.error(err)); // TypeError: console.xxx is not a function
- 또한
45.5 프로미스 체이닝
후속 처리 메서드는 언제나 프로미스를 반환하므로 연속적으로 호출할 수 있는 것
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
const url = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com'; // id가 1인 post의 userId를 취득 promiseGet(`${url}/posts/1`) // 취득한 post의 userId로 user 정보를 취득 .then(({ userId }) => promiseGet(`${url}/users/${userId}`)) .then(userInfo => console.log(userInfo)) .catch(err => console.error(err));
후속 처리 메서드 콜백 함수의 인수 후속 처리 메서드의 반환값 then promiseGet 함수가 반환한 프로미스가 resolve한 값
⇒ id가 1인 post콜백 함수가 반환한 프로미스 then 첫 번째 then 메서드가 반환한 프로미스가 resolve한 값
⇒ post의 userId로 취득한 user 정보콜백 함수가 반환한 값(undefined)을 resolve한 프로미스 catch
(에러가 발생해야 호출)promiseGet 함수 또는 앞선 후속 처리 메서드가 반환한 프로미스가 reject한 값 콜백 함수가 반환한 값(undefined)을 resolve한 프로미스 - 후속 처리 메서드는 콜백 함수가 프로미스가 아닌 값을 반환해도 그 값을 암묵적으로
resolve또는reject하여 프로미스를 생성해 반환
- 후속 처리 메서드는 콜백 함수가 프로미스가 아닌 값을 반환해도 그 값을 암묵적으로
콜백 패턴은 가독성이 좋지 않고 콜백 헬이 발생하지만, 프로미스 체이닝은 그렇지 않다.
ES8에서 도입된
async/await을 이용하면 콜백 패턴의 가독성 문제를 해결하고, 후속 처리 메서드 없이 프로미스가 처리 결과를 반환하도록 구현할 수 있다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
const url = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com'; (async () => { // id가 1인 post의 userId를 취득 const { userId } = await promiseGet(`${url}/posts/1`); // 취득한 post의 userId로 user 정보를 취득 const userInfo = await promiseGet(`${url}/users/${userId}`); console.log(userInfo); })();
45.6 프로미스의 정적 메서드
45.6.1 Promise.resolve/Promise.reject
- 이미 존재하는 값을 래핑하여 프로미스 생성
Promise.resolve- 인수로 전달받은 값을
resolve하는 프로미스 생성
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
// 배열을 resolve하는 프로미스를 생성 const resolvedPromise = Promise.resolve([1, 2, 3]); resolvedPromise.then(console.log); // [1, 2, 3] // 위 코드는 다음 코드와 동일하게 동작한다. const resolvedPromise = new Promise(resolve => resolve([1, 2, 3])); resolvedPromise.then(console.log); // [1, 2, 3]
- 인수로 전달받은 값을
Promise.reject- 인수로 전달받은 값을
reject하는 프로미스 생성
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
// 에러 객체를 reject하는 프로미스를 생성 const rejectedPromise = Promise.reject(new Error('Error!')); rejectedPromise.catch(console.log); // Error: Error! // 위 코드는 다음 코드와 동일하게 동작한다. const rejectedPromise = new Promise((_, reject) => reject(new Error('Error!'))); rejectedPromise.catch(console.log); // Error: Error!
- 인수로 전달받은 값을
45.6.2 Promise.all
여러 개의 비동기 처리를 모두 병렬 처리할 때 사용
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
const requestData1 = () => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 3000)); const requestData2 = () => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(2), 2000)); const requestData3 = () => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(3), 1000)); // 세 개의 비동기 처리를 순차적으로 처리 const res = []; requestData1() .then(data => { res.push(data); return requestData2(); }) .then(data => { res.push(data); return requestData3(); }) .then(data => { res.push(data); console.log(res); // [1, 2, 3] ⇒ 약 6초 소요 }) .catch(console.error); // 세 개의 비동기 처리를 병렬로 처리 Promise.all([requestData1(), requestData2(), requestData3()]) .then(console.log) // [ 1, 2, 3 ] ⇒ 약 3초 소요 .catch(console.error);
- 인수: 프로미스 요소를 갖는 이터러블 (배열 등)
- 반환: 전달받은 프로미스의 처리 결과를 담은 배열을
resolve하는 새로운 프로미스- 전달받은 프로미스가 모두
fulfilled상태가 되면 모든 처리 결과를 배열에 저장한다. - 이때 첫 번째 프로미스 처리 결과부터 순서대로 배열에 저장한다.
- 전달받은 프로미스가 모두
- 전달받은 프로미스에서 하나라도
rejected상태가 되면 즉시 종료- 에러를
reject하는 새로운 프로미스 반환
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Promise.all([ new Promise((_, reject) => setTimeout(() => reject(new Error('Error 1')), 3000)), new Promise((_, reject) => setTimeout(() => reject(new Error('Error 2')), 2000)), new Promise((_, reject) => setTimeout(() => reject(new Error('Error 3')), 1000)) ]) .then(console.log) .catch(console.log); // Error: Error 3
- 에러를
인수로 전달받은 이터러블의 요소가 프로미스가 아닌 경우 ⇒
Promise.resolve메서드를 통해 프로미스로 래핑1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Promise.all([ 1, // => Promise.resolve(1) 2, // => Promise.resolve(2) 3 // => Promise.resolve(3) ]) .then(console.log) // [1, 2, 3] .catch(console.log);
예제
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// GET 요청을 위한 비동기 함수
const promiseGet = url => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET', url);
xhr.send();
xhr.onload = () => {
if (xhr.status === 200) {
// 성공적으로 응답을 전달받으면 resolve 함수를 호출한다.
resolve(JSON.parse(xhr.response));
} else {
// 에러 처리를 위해 reject 함수를 호출한다.
reject(new Error(xhr.status));
}
};
});
};
const githubIds = ['jeresig', 'ahejlsberg', 'ungmo2'];
Promise.all(githubIds.map(id => promiseGet(`https://api.github.com/users/${id}`)))
// [Promise, Promise, Promise] => Promise [userInfo, userInfo, userInfo]
.then(users => users.map(user => user.name))
// [userInfo, userInfo, userInfo] => Promise ['John Resig', 'Anders Hejlsberg', 'Ungmo Lee']
.then(console.log)
.catch(console.error);
45.6.3 Promise.race
- 인수: 프로미스 요소를 갖는 이터러블 (배열 등)
반환: 가장 먼저
fulfilled상태가 된 프로미스의 처리 결과를resolve하는 새로운 프로미스1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Promise.race([ new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 3000)), // 1 new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(2), 2000)), // 2 new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(3), 1000)) // 3 ]) .then(console.log) // 3 .catch(console.log);
- 전달받은 프로미스에서 하나라도
rejected상태가 되면 즉시 종료- 에러를
reject하는 새로운 프로미스 반환
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Promise.race([ new Promise((_, reject) => setTimeout(() => reject(new Error('Error 1')), 3000)), new Promise((_, reject) => setTimeout(() => reject(new Error('Error 2')), 2000)), new Promise((_, reject) => setTimeout(() => reject(new Error('Error 3')), 1000)) ]) .then(console.log) .catch(console.log); // Error: Error 3
- 에러를
45.6.4 Promise.allSettled
- 인수: 프로미스 요소를 갖는 이터러블 (배열 등)
- 반환: 전달받은 프로미스의 처리 결과를 담은 배열
전달받은 프로미스가 모두
settled상태가 되면 모든 처리 결과를 배열에 저장한다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Promise.allSettled([ new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 2000)), new Promise((_, reject) => setTimeout(() => reject(new Error('Error!')), 1000)) ]).then(console.log); /* [ {status: "fulfilled", value: 1}, {status: "rejected", reason: Error: Error! at <anonymous>:3:54} ] */
처리 결과 객체
fulfilled상태:status프로퍼티(비동기 처리 상태)와value프로퍼티(처리 결과)rejected상태:status프로퍼티(비동기 처리 상태)와reason프로퍼티(에러)
1 2 3 4 5 6
[ // 프로미스가 fulfilled 상태인 경우 {status: "fulfilled", value: 1}, // 프로미스가 rejected 상태인 경우 {status: "rejected", reason: Error: Error! at <anonymous>:3:60} ]
45.7 마이크로태스크 큐
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
setTimeout(() => console.log(1), 0);
Promise.resolve()
.then(() => console.log(2))
.then(() => console.log(3));
// 2 -> 3 -> 1 순으로 출력
- 프로미스의 후속 처리 메서드의 콜백 함수는 마이크로태스크 큐에 일시 저장
- 그 외의 비동기 함수의 콜백 함수, 이벤트 핸들러는 태스크 큐에 일시 저장
- 마이크로태스크 큐가 태스크 큐보다 우선순위가 높다.
- 콜 스택이 비면 이벤트 루프는 마이크로태스크 큐에서 대기 중인 함수를 먼저 가져온다.
45.8 fetch
- HTTP 요청 전송 기능을 제공하는 클라이언트 사이드 Web API
XMLHttpRequest객체보다 사용법이 간단하고, 프로미스를 지원해 콜백 패턴의 단점에서 벗어난다.
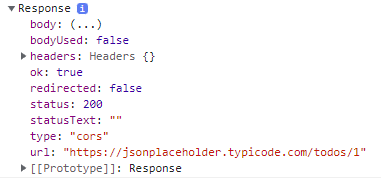
fetch(url[, options])url: HTTP 요청을 전송할 URLoptions: HTTP 요청 메서드, HTTP 요청 헤더, 페이로드 등을 설정한 객체- 반환: HTTP 응답을 나타내는
Response객체를 래핑한Promise객체
1 2
fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1') .then(response => console.log(response));
Response.prototypeResponse객체의 HTTP 응답 몸체를 위한 메서드 제공Response.prototype.json메서드- MIME 타입이
application/json인 HTTP 응답 몸체를 취득하여 역직렬화
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1') // response는 HTTP 응답을 나타내는 Response 객체이다. // json 메서드를 사용하여 Response 객체에서 HTTP 응답 몸체를 취득하여 역직렬화한다. .then(response => response.json()) // json은 역직렬화된 HTTP 응답 몸체이다. .then(json => console.log(json)); // {userId: 1, id: 1, title: "delectus aut autem", completed: false}
- MIME 타입이
에러 처리
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
const wrongUrl = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/XXX/1';
// 부적절한 URL이 지정되었기 때문에 404 Not Found 에러가 발생한다.
fetch(wrongUrl)
.then(() => console.log('ok'))
.catch(() => console.log('error'));
// ok
fetch함수가 반환하는 프로미스는 HTTP 에러가 발생하면ok상태를false로 설정한Response객체를resolve한다.- 404 Not Found나 500 Internal Server Error와 같은 HTTP 에러가 아닌, 오프라인 등의 네트워크 장애나 CORS 에러에 의해 요청이 완료되지 못한 경우에만 프로미스를
reject 따라서
ok상태를 확인해 명시적으로 에러를 처리해야 한다.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
const wrongUrl = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/XXX/1'; // 부적절한 URL이 지정되었기 때문에 404 Not Found 에러가 발생한다. fetch(wrongUrl) // response는 HTTP 응답을 나타내는 Response 객체다. .then(response => { if (!response.ok) throw new Error(response.statusText); return response.json(); }) .then(todo => console.log(todo)) .catch(err => console.error(err));
- 404 Not Found나 500 Internal Server Error와 같은 HTTP 에러가 아닌, 오프라인 등의 네트워크 장애나 CORS 에러에 의해 요청이 완료되지 못한 경우에만 프로미스를
- 참고) axios
- 모든 HTTP 에러를
reject하는 프로미스 반환 → 모든 에러를catch에서 처리 가능 - 인터셉터, 요청 설정 등 다양한 기능 지원
- 모든 HTTP 에러를
1. GET 요청
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
const request = {
get(url) {
return fetch(url);
},
post(url, payload) {
return fetch(url, {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify(payload)
});
},
patch(url, payload) {
return fetch(url, {
method: 'PATCH',
headers: { 'content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify(payload)
});
},
delete(url) {
return fetch(url, { method: 'DELETE' });
}
};
request.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1')
.then(response => {
if (!response.ok) throw new Error(response.statusText);
return response.json();
})
.then(todos => console.log(todos))
.catch(err => console.error(err));
// {userId: 1, id: 1, title: "delectus aut autem", completed: false}
2. POST 요청
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
request.post('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos', {
userId: 1,
title: 'JavaScript',
completed: false
}).then(response => {
if (!response.ok) throw new Error(response.statusText);
return response.json();
})
.then(todos => console.log(todos))
.catch(err => console.error(err));
// {userId: 1, title: "JavaScript", completed: false, id: 201}
3. PATCH 요청
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
request.patch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1', {
completed: true
}).then(response => {
if (!response.ok) throw new Error(response.statusText);
return response.json();
})
.then(todos => console.log(todos))
.catch(err => console.error(err));
// {userId: 1, id: 1, title: "delectus aut autem", completed: true}
4. DELETE 요청
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
request.delete('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1')
.then(response => {
if (!response.ok) throw new Error(response.statusText);
return response.json();
})
.then(todos => console.log(todos))
.catch(err => console.error(err));
// {}