Chapter 1: A Tour of Computer Systems
1.1 Information Is Bits + Context
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello, world\n");
return 0;
}
- Text files
- 위
hello.c파일처럼 ASCII 문자만을 포함한 파일
- 위
- Binary files
- Text file이 아닌 파일
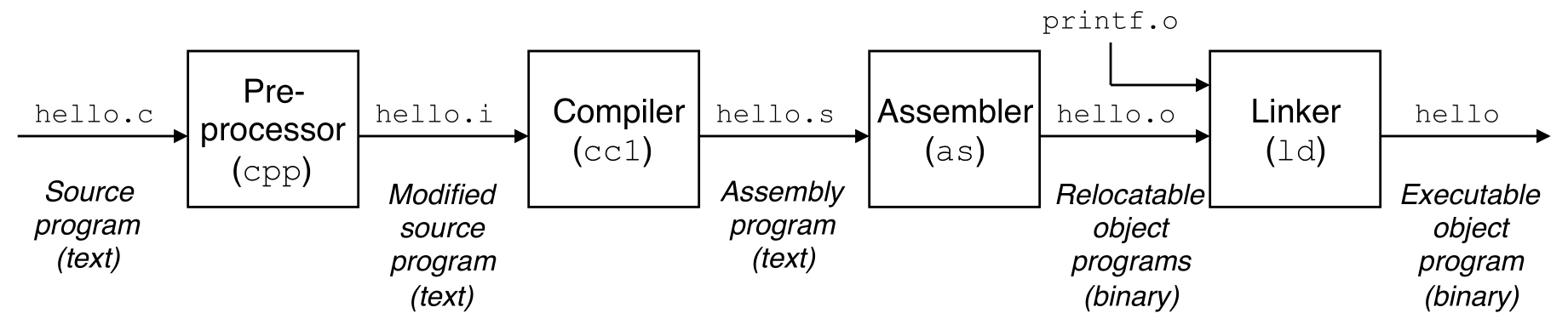
1.2 Programs Are Translated by Other Programs
into Different Forms
hello.c를 실행하기 위해선 이를 machine-language로 변환한 뒤 executable object program으로 패키징해야 한다.
Preprocessor, compiler, assembler, linker 작업을 수행하는 프로그램을 compilation system이라 한다.
- Preprocessing phase
- C 프로그램을
#으로 시작하는 directive에 따라 수정 - 일반적으로
.i으로 끝나는 또 다른 C 프로그램이 결과로 나옴
- C 프로그램을
- Compilation phase
- Assembly-language program을 포함한
hello.s텍스트 파일로 변환 - 다른 high-level 언어라도 같은 assembly 언어 결과물을 내놓음
- Assembly-language program을 포함한
- Assembly phase
- Machine-language instruction으로 변환 후 relocatable object program으로 패키징한 뒤 결과물을
hello.o파일로 내놓음 - 이때 결과 파일은 binary 파일이므로 사람이 읽을 수 없음
- Machine-language instruction으로 변환 후 relocatable object program으로 패키징한 뒤 결과물을
- Linking phase
printf.o에 속하는printf함수는 사용할 수 있도록 이를 합치는 과정hello파일이 결과로 생성되며 이 파일이 executable object file이다. 이제 메모리에 올려 시스템이 실행할 수 있다.
1.3 It Pays to Understand How Compilation Systems Work
왜 compilation system의 동작 방식을 이해해야 하는가?
- Optimizing program performance
- Machine-level 코드에 대한 기초를 이해한다면 더 효율적인 코드를 작성할 수 있다.
- Understanding link-time errors
- Linker에서 나오는 에러를 이해할 수 있다.
- Avoiding security holes
- 프로그램 스택에 데이터가 저장되는 방식을 이해해야 안전한 프로그래밍을 할 수 있다.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.